Low End Tidal Co2 Acidosis
This is going to increase the elimination of co2. Generally speaking, a rise in paco2 of 10mmhg will result in a ph decrease of 0.1.


Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm hg for partial co2 pressure in the arterial blood.


Low end tidal co2 acidosis. 40mcg of narcan at this point might only reverse respiratory depression which is great, but it can (i’ve experienced this first hand) also elevate the. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time (resulting in overdistention), or from such circulatory problems as shock, massive fluid loss, or pump. To modify co2 content in blood one needs to modify alveolar ventilation.
The patient is simply not producing enough co2! The body’s physiologic response is to increase respiratory rate to attenuate the metabolic acidosis. Is co2 high or low in metabolic acidosis.
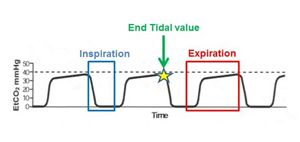
The use of end tidal co2 readings. •artificially ventilated patient when the ventilator is running at a low rate and a high minute volume •in patients with spontaneous respiration with: Acidosis with high co2 and low bicarb.
•beginning of plateau is low •end of plateau shows a peak (ppv pushes co 2 to monitor) •may see similar pattern in obesity or pregnancy return of spontaneous ventilation during cpr: This increased respiratory rate “blows off” carbon dioxide and lowers etco 2. The co 2 waveform is a valuable tool for detecting leaks in the anesthetic system, rebreathing of co 2
To do this, the tidal volume or the respiratory rate may be tampered with (t low and p low in aprv). The patient is producing too much. But in a patient with intact respiratory drive, they're going to respond to the acidosis by increasing their tidal volume and respiratory rate.
To compensate for metabolic acidosis, patients increase their minute ventilation. If the co 2 absorbing lime bucket is saturated, the circuit becomes inundated with expired co 2 and the baseline gradually increases. Low end tidal co2 acidosis.
Definition of low co2 (hypocapnia) hypocapnia (hypocapnea, also known as hypocarbia) is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. Respiratory acidosis is an acid balance disorder due to alveolar hypoventilation. Prolonged hypercapnia will lead to respiratory acidosis as there is a linear relationship between paco2 and ph.
So our paco2 ends up being determined by the balance between co2 production (increased by acidosis), and co2 elimination (increased by hyperventilation / tachypnea). Why is end tidal co2 lower than paco2? Raising the rate or the tidal volume, as well as increasing t low, will increase ventilation and decrease co2.
Recirculated co2 due to a saturated co2 absorber. Carbon dioxide production occurs rapidly and failure of. Why is co2 low in metabolic acidosis.
This is a major respiratory symptom. Low co2 acidosis or alkalosis. Etco2 measurements can be very useful in the narcotic overdose, a patient can have an etco2 of 70mmhg but have spo2 of 99% with assisted ventilations.








0 Response to "Low End Tidal Co2 Acidosis"
Post a Comment